how do search engines work?
how do search engines work?
Search engines work through three primary functions:
- Crawling: Scour the Internet for content, looking over the code/content for each URL they find.
- Indexing: Store and organize the content found during the crawling process. Once a page is in the index, it’s in the running to be displayed as a result to relevant queries.
- Ranking: Provide the pieces of content that will best answer a searcher’s query, which means that results are ordered by most relevant to least relevant.
What is search engine crawling?
Crawling is the discovery process in which search engines send out a team of robots (known as crawlers or spiders) to find new and updated content. Content can vary — it could be a webpage, an image, a video, a PDF, etc. — but regardless of the format, content is discovered by links.
Googlebot starts out by fetching a few web pages, and then follows the links on those webpages to find new URLs. By hopping along this path of links, the crawler is able to find new content and add it to their index called Caffeine — a massive database of discovered URLs — to later be retrieved when a searcher is seeking information that the content on that URL is a good match for.
What is a search engine index?
Search engines process and store information they find in an index, a huge database of all the content they’ve discovered and deem good enough to serve up to searchers.
Search engine ranking
When someone performs a search, search engines scour their index for highly relevant content and then orders that content in the hopes of solving the searcher’s query. This ordering of search results by relevance is known as ranking. In general, you can assume that the higher a website is ranked, the more relevant the search engine believes that site is to the query.
It’s possible to block search engine crawlers from part or all of your site, or instruct search engines to avoid storing certain pages in their index. While there can be reasons for doing this, if you want your content found by searchers, you have to first make sure it’s accessible to crawlers and is indexable. Otherwise, it’s as good as invisible.
By the end of this chapter, you’ll have the context you need to work with the search engine, rather than against it!
Crawling: Can search engines find your pages?
As you’ve just learned, making sure your site gets crawled and indexed is a prerequisite to showing up in the SERPs. If you already have a website, it might be a good idea to start off by seeing how many of your pages are in the index. This will yield some great insights into whether Google is crawling and finding all the pages you want it to, and none that you don’t.
One way to check your indexed pages is “site:yourdomain.com”, an advanced search operator. Head to Google and type “site:yourdomain.com” into the search bar. This will return results Google has in its index for the site specified:
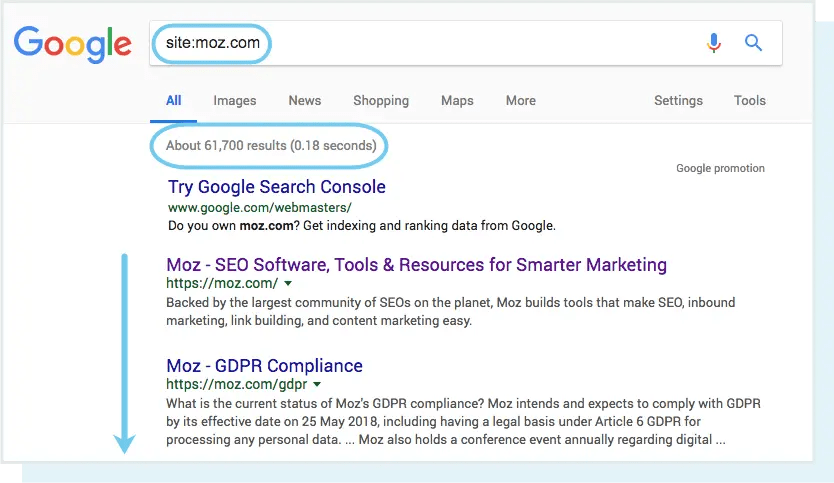
The number of results Google displays (see “About XX results” above) isn’t exact, but it does give you a solid idea of which pages are indexed on your site and how they are currently showing up in search results.
For more accurate results, monitor and use the Index Coverage report in Google Search Console. You can sign up for a free Google Search Console account if you don’t currently have one. With this tool, you can submit sitemaps for your site and monitor how many submitted pages have actually been added to Google’s index, among other things.
If you’re not showing up anywhere in the search results, there are a few possible reasons why:
- Your site is brand new and hasn’t been crawled yet.
- Your site isn’t linked to from any external websites.
- Your site’s navigation makes it hard for a robot to crawl it effectively.
- Your site contains some basic code called crawler directives that is blocking search engines.
- Your site has been penalized by Google for spammy tactics.